When thinking through social software (also known as social computing, social media, and social web) I have been influenced by many ideas, but at the core there are two things that stick in my head: 1) Good visualization; and 2) Object-centered sociality. Getting the two to mesh, while accounting for most of the important components of social software has been really difficult for me to square for quite some time.
One of my starting point for visualization has been Gene Smith's wonderful honeycomb adaption of the social software building blocks. The strength of the graphic is having identity at the core of the social interaction. The honeycomb allows Gene to display many different services deployed has the pieces of the social software stack (stack is a collection of elements that comprise a whole set of services).
One of the things with Gene's graphic that has always bugged me is I have not been able to square it with the object also being at the center of the social interaction. A second piece that also bothered me is it did not account for the action element of collaboration (people working together as part of a group or team to build something, while acting with one goal as their focus, which can be a broad goal). Collaboration is central to nearly every enterprise or work organization effort (directly or tangentially) I am or have been involved in professionally, so I feel it is essential to include it.
Object-Centered Sociality
It was through reading Jyri Engeström's blog post about "Why some social network services work and others don't — Or: the case for object-centered sociality" that I came to have familiarity with Karin Knorr Cetina's object-centered sociality. It was through the repeated mentioning of this Knorr Cetina concept by Rashmi Sinha in her presentations and from personal conversations with Rashmi that the ideas deep value sunk in (it is a concept central to Rashmi and Jon Boutelle's product SlideShare).
Knorr Cetina's work brings into view the individual and the object as central elements in social interaction. She proposes physical objects, around which discussions take place help focus and start conversation and other social interaction between and among people. In her and Urs Bruegger's journal article "The Market as an Object of Attachment: Exploring Postsocial Relations in Financial Markets" in Canadian Journal of Sociology 25, 2 (2000): 141-168, they state:
One characteristic of the present situation is that perhaps for the first time in recent history it appears unclear whether other persons are, for human beings, the most fascinating part of their environment. Objects may also be the risk winners of the relationship risks which may authors find inherent in contemporary human relations.
The short of this is the person may not be the sole focus and possibly the person is not the focus of social interaction as the objects being discussed in social interactions is the focus for the people and take the role of the most interesting element in the social discourse.
When we look at social web services like Flickr we see the photos that a person takes and shares are the focus of social interaction. It is around these objects that the conversation takes place. Jyri Engeström calls these objects of social focus "social objects".
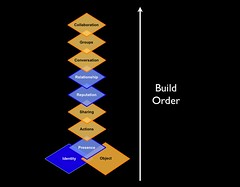
It is these social objects that are in need of being accounted for in a visualization of the social software stack. While in Germany for the most recent IA Konferenz I wanted to include his more fleshed out understanding of the social software stack, in this case it is actions or components that comprise sociality from the perspective on an individual in a social environment. I really wanted a graphic that brought these elements together so I could talk through it more easily in a workshop on the foundations of social software and tagging. The visual model is this Venn diagram that I put together sitting in the hallway for an hour or so. While it is not as interesting as Gene's graphic, for me it is a much better representation of the important components in social software if your goal is wanting your service/software to work optimally.
Explaining the Graphic
 Yes, the inclusion of the object into the graphic is given a central focus equal to that of identity. Identity and the object are the two important elements that comprise the social software stack. All elements that are represented in the graphic may or could be seen by others and are triggers for social interaction with other people (yes, the interaction can be with just other objects, but that is another subject I am not addressing in this writing). This ability to see all the elements represented is the social aspect of the software service. The overlaps are where there are direct interactions. But, there is a specific order to the revealing and relevance of each of the elements after the identity and object are shown.
Yes, the inclusion of the object into the graphic is given a central focus equal to that of identity. Identity and the object are the two important elements that comprise the social software stack. All elements that are represented in the graphic may or could be seen by others and are triggers for social interaction with other people (yes, the interaction can be with just other objects, but that is another subject I am not addressing in this writing). This ability to see all the elements represented is the social aspect of the software service. The overlaps are where there are direct interactions. But, there is a specific order to the revealing and relevance of each of the elements after the identity and object are shown.
The order is important because if one leaves out an element (or does not account for the elements in some manner) the next step is really not going to be capable of being fully realized and there will be a weakness in the social software. I can not stress this enough, this is not a list of items to pick from, but if you want to have reputation in the system there previous elements really need to be in place or accounted for through using an outside service that can be pointed to or brought into the service through using an outside service.
Order of the Elements
The order is: Identity and Object; Presence; Actions; Sharing; Reputation; Relationships; Conversation; Groups; and Collaboration.
The colors were chosen so the bridging elements were orange and fit with the color scheme of my company and the usual slide templates I use when presenting (orange with blue highlights, text, and accents). After I built the graphic I realized the similarity to a finance industry logo, but when playing with other color combinations the graphic lost its punch and also did not fit within the color scheme of my long used slide template, so I have left the colors alone.
The Elements in the Social Software Stack
The Central Focus
Identity
Identity is comprised of the information about the person using the social software tool. Often the identity is a built upon profile information such as name, username, location, personal website, e-mail, photo or avatar, and sometimes the person's age. These pieces help others recognize the person and can carry associations from other interactions and/or services to the current service (that is if the individual wants this cross-service tracking). Contact information is normally required for setting up an account so the service (and the people running the service) can communicate with the person. Sometimes the contact information is shared if the person using the service permits the sharing of the contact information with other people using the software/service.
Identity is also augmented through the inclusion of usernames on other services and sites the person contributes to or has an account on. This cross-service identity helps people who use other services to find their friends and contacts more easily. The cross-service identity also helps tie others understanding of the identity and possibly reputation as understood by other people. Cross-service identity connecting can also be used for aggregating content that an identity shared on another service into a new service.
Identity is included in the focus on object-centered sociality as it is people who are being social around the object. It seems that there is a codependent relationship between the person (their perceptions as expressed through their interest and actions around and about an object). The identity is a pivot to learn more about these understandings for a richer understanding by those reading/consuming what has been shared. This is much like the object is a pivot to find others who have interest in the same type of things.
Object
The object is the core focus of object-centered sociality and in this representation with one identity interacting it is part of the the codependent at the core of the graphic. The object is the center of the sociality. The object is what is being shared with others. This shared object may be a photo, bookmark/link, video, statement, or other matter. The object may be digital or non-digital in nature. Lastly, the object can also be what is being built in a collaboration-focussed effort.
Active Elements
Now that we have the cornerstone set of the two main components for sociality we can start looking at the elements around these two components. Again, these actions and elements are in a specific order that build upon the previous elements. These are active elements because they are either actions or are the result of sets of actions.
Presence
The identity is often built around static profile information, but people are not static as they have lives they lead and people have locations and tasks they perform that provide context for understanding perspective of statements or related actions. Presence can be a simple as Twitter's question of "what are you doing?" It can also be location, time, availability, and/or activity. These provide others a glimpse of understanding, or at least a hint of the identity's perspective.
In the case of Twitter and similar services the statement of presence is not necessarily related to another object, but the presence statement in and of itself acts as the object. In the case where presence is the object, the object is directly related to the person and not an external object. The presence statements may or may not be shared with others as the understanding is quite helpful information for the individual for later recollection as to why they made other statements or actions.
Actions
Using stated presence or the inferred presence, as the actions connote presence around an object that action is taking place around. The actions are what is being done as an expression communicating to one's self or to others what they understand. This may be as simple as just expressing interest (even if the interest is negative). These actions are expressions of the person's understanding can take the form of annotation, messaging, modification of the object, commenting, rating, tagging, flagging or favoring, storing, naming, etc. The actions are tied to the person who is taking the action and linked to the object around which they are taking the action. These actions are are in most cases the some form of adding data or meta data to or around the object.
In social bookmarking in del.icio.us the object is the link expressed as the URL and the person is taking the action of saving the link and is likely also annotating and tagging that link for at least their own retrieval.
The actions always include the identity and the object (which may be the person's own identity and presence). Actions may or may not be shared with others. As many services provide public, selective, and private access to the information and actions.
Sharing
The act of sharing is where we finally start fully acknowledging social actions. The presence and actions elements can be private, if the person behind the identity wishes. Sharing is the social action that opens up the capability for all others (or only others whom have been given permission) to see their actions and possibly presence around an object. This can also include opening access to an object for others to see and others to add their annotations and actions around the object. This includes open annotations of other's openly shared objects or objects shared to a closed community to which the person has access.
Reputation
Shared presence and actions are the elemental building blocks for reputation. Reputation can build upon something as simple as existence on a service, by having an identity there. Reputation grows based on the interpretation of others based on shared presence and actions.
The actions that build reputation can be through the content that has been created by that identity. Others' understanding grows through seeing annotations that are by an identity (ratings, notes, comments, what is shared, etc.). Others also see actions that have been attributed to the identity, which may not be the direct actions that are seen, but can be actions of stating a relationship, joining a group, rewards (top contributor, etc.), or other indirectly perceived action.
The volume of actions also builds reputation. This can be the breadth of actions or breadth of subjects covered. Volume can also be depth of actions. Depth is how many in a subject area and/or the depth of understanding showed on a subject.
The breadth and depth lead to understanding of quality. Quality is often attributed by others based on their own perceptions and understanding. Perceptions, as we know, vary from person to person and that builds trends of reputation. Quality is also interpreted through perception. These interpretations are can be reflected in what others actions taken around an identity (identity can be the focal object in this activity) such as rating contributions made by an identity, favoriting/holding on to the actions of an identity (comments, their favorites, etc.), electing to follow the actions through subscribing or other similar actions, etc. Others may also write about an identity to express and understanding of the identity.
Relationships
Based on reputation people chose to interact with that identity. Through interaction relationships are established or built. This may be explicitly stated in some manner (the "connection" or "collaborator" or "friend" distinctions in some social services are examples). Relationships may also be an inferred relationship based upon actions. The inferred relationship is through another's actions of following, subscribing to actions, annotating an object, or other actions.
Relationships may be causal (as result of actions) or intended. The breadth of the relationship needs also be considered. A relationship between people or their identities can be based only on a precise subject matter or many distinct subjects in a granular social manner. The relationship may be more broad-line by encompassing most subjects that around a person and their identity.
There is rich derived value that can be built upon through identifying and understanding the granular subjects of common interest between people. The relationship can be one that is expansive, in that one person or both are learning and exploring new ideas and material through the shared experiences and shared understanding of the other. Understanding that a relationship is only as broad as a similar interest(s) (it does not have to be the same polarity (like/dislike)) such as for acoustic bebop jazz will help framing the relationship for what is shared, followed, and interaction made around.
Conversation
A relationship predicated on some understanding of reputation (remembering that it may be a rather thin understanding of reputation) provides a good foundation the next stage, conversation. The conversation is most often with an identity about or around an object.
The conversation may be a 2-way or multi-directional. This communication may be a synchronous live conversation or asynchronous over time (message boards or other services what allow comments or time ordered annotations. The conversation in a social environment is open and often around an object (keeping in mind the object may be a person's presence statements as in Twitter).
These conversations may be structured through form-based forums or listserves. The conversations may be free-form as in Consumating'sflirting through tagging or other open communication structures.
Groups
It is in the conversation (derived from relationships based on reputation) that people with similar interest come to the point where they want a more formal relationship so to have more focussed communication and sharing and these people form a group. The group is a sub-set of the whole service, as in Ma.gnolia's groups for sharing social bookmarks (Ma.gnolia's groups can be open to all or they can be closed and not seen). The sharing is a collective understanding of the group with each individual identity openly sharing their actions around that subject matter or interest. The group is normally comprised of trusted listeners who have a relatively strong understanding of reputation. The group is a collective voice what accounts for each voice. There does not have to be a common goal other than sharing information around (tightly or broadly clinging to the subject of interest) and each voice matters in the group.
Collaboration
Groups working often leads to collaboration where not only are people openly sharing information as individuals, but aim to work together to build objects. One example of this is a wiki where there the object is the development of a page or set of pages built through a collaborative process. The collaborative process has one goal (explaining a subject in the case of a wiki) and the group works with a single focus and intentionally becomes a single voice. The object being built may be text content, video with different production tasks and skills needed, other media, an application or service, or other object (physical or digital). Central to collaboration is an understanding of what is being built. Collaboration is most often iterative though building upon what is there with the goal of improving it.
Summary
A walk through the elements in the social software stack should provide an understanding of the progressive relationship between the elements. The aim is for this to be used a guide to think through building and implementing social software. I talk to many organizations that are trying to get to collaboration but are missing some or many pieces of the social software stack that collaboration is built upon. Not all of the elements need to be in the same tool, but they need to be accounted for in an environment that is collaborating.
Those not building collaborative services will also greatly benefit from understanding at what stage their social software service or tool is aiming to serve and ensuring all of the preceding elements are included or accounted for in the service.
Lastly, but not least it is important to understand what is the object of focus in the social software tool or service. This social object is part of the starting foundation and the better the understanding of the object and how it works in the service or tool the better the whole of the project/product will be in the end.
![Reblog this post [with Zemanta]](http://img.zemanta.com/reblog_e.png?x-id=bd9f1992-c787-4b5d-a922-86e42aa50855)